Contamination Control
JSC scientist Mike Zolensky took the lead in formulating and implementing the Contamination Control Plan for the Stardust Mission. This plan was the blueprint for ensuring that the returned samples remain as pristine as possible for current and future scientific studies.
A significant constraint on any sample return mission is the absolute requirement for a contamination-free sample container. Calculations indicate that for a chondritic composition sample weighing 1 µg, the total permitted contamination levels for inorganic elements on the walls of the sample container vary from 10-9 to 10-16 g. For nanogram-sized grains the requirements are significantly more stringent. Accordingly, new and small-scale analytical techniques such as ion probe analysis, proton induced X-ray emission analysis (PIXE), and resonance ionization mass spectrometry (RIMS) require even more care in contamination control. For organic compounds, contamination control requirements are both difficult to define and hard to achieve.
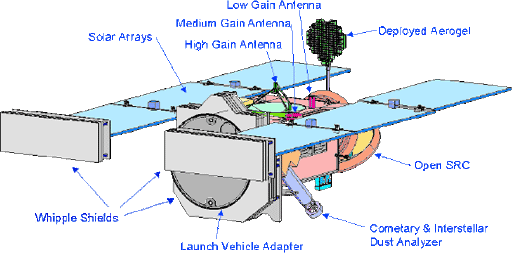
Stardust spacecraft, indicating principal components. The image shows the aerogel collector deployed, ready to collect dust.
